Learning objective
- To understand how binary is used to store different types of data.
Success criteria
- I can explain that binary stores many types
This content is for subscribers only. Join for access today.
National curriculum
Computing
Pupils should be taught to:
- Understand
This content is for subscribers only. Join for access today.
Cross-curricular links
Mathematics
Number – multiplication
This content is for subscribers only. Join for access today.
Before the lesson
This content is for subscribers only. Join for access today.
Lesson plan
Recap and recall
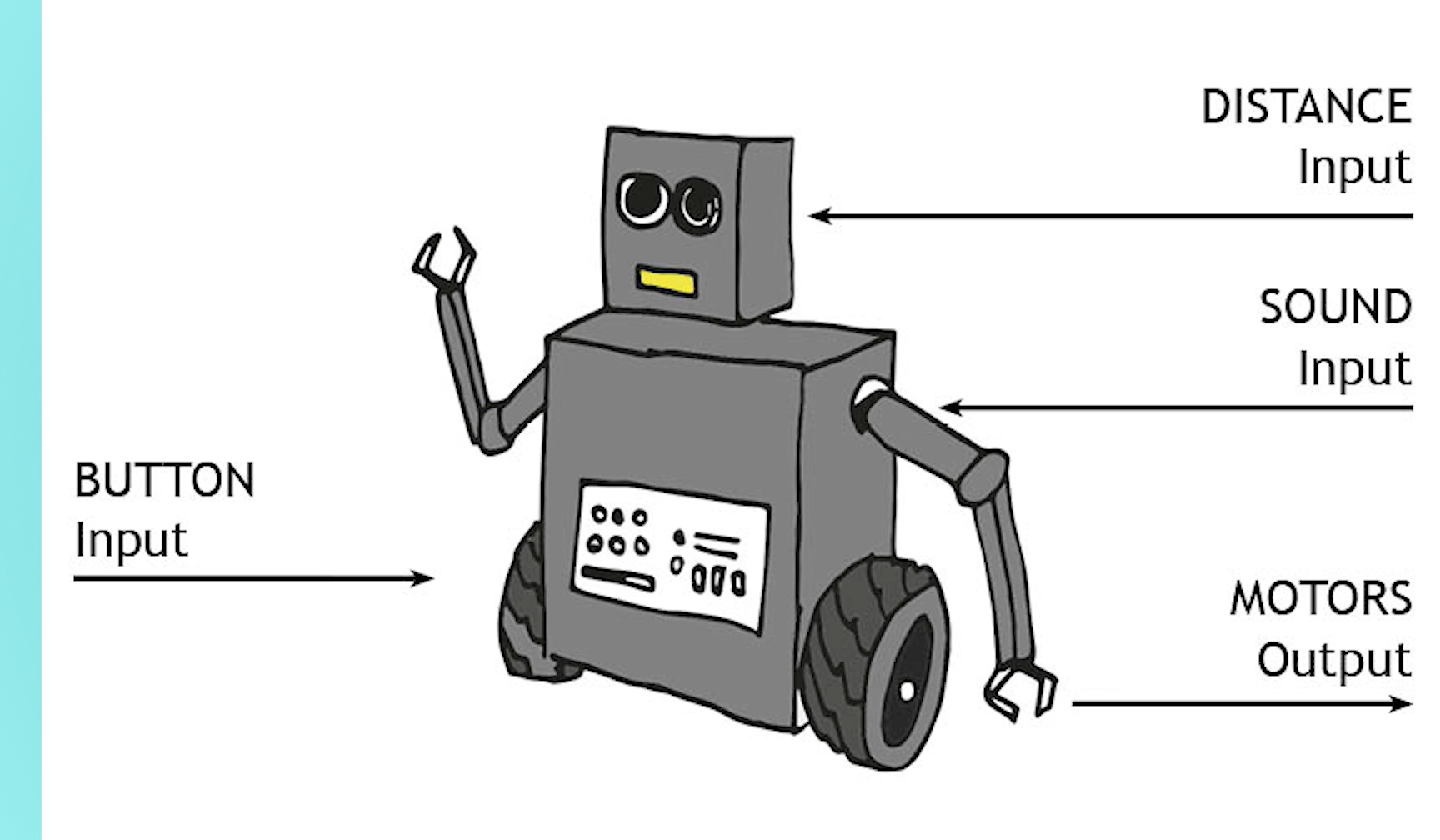
Explain that the children will be thinking back to what they learnt about computer architecture in the previous lesson. Display the Presentation: Explain the answer and read the statement aloud. Ask the children to discuss the statement with a partner and explain why it might be true, using what they remember about input, processing, output…
This content is for subscribers only. Join for access today.
Extended-mode explainer videos
How to extend your display to view the lesson page and presentation mode simultaneously. Choose your operating system below to watch the video
If you need further support with extending your display,
please contact [email protected].
Extended-mode explainer video: For Mac
Extended-mode explainer video: For Windows
Adaptive teaching
Pupils needing extra support
- Could use the Resource: Data size cards: support version to order a reduced number of items by comparing one size at a time, reducing cognitive load while still meeting the success criteria.
- Could re-watch the link: Bytes in perspective to reinforce relative data sizes by using the visual comparison as a reference during sorting and discussion.
Pupils working at greater depth
- Should justify their data size choices using direct comparisons (for example, explaining why a video file needs more storage than a sound file) by referring to the amount and type of information stored.
- Could draw a labelled visual representation (for example, bars or scaled blocks) to show how a bit compares to a byte, kilobyte and megabyte.
This content is for subscribers only. Join for access today.
Assessing progress and understanding
Pupils with secure understanding indicated by: explaining that binary is used to
This content is for subscribers only. Join for access today.
Vocabulary definitions
-
bit
A single 0 or 1, which is the smallest piece of data a computer can store.
-
binary
A system computers use to store information using only 0 and 1.
This content is for subscribers only. Join for access today.
In this unit
Assessment - Computing Y5: Mars Rover 1
Lesson 1: Mars Rover
Lesson 2: Binary code
Lesson 3: Computer architecture
Lesson 4: How computers store data using binary
Lesson 5: Using binary - text
Contributors